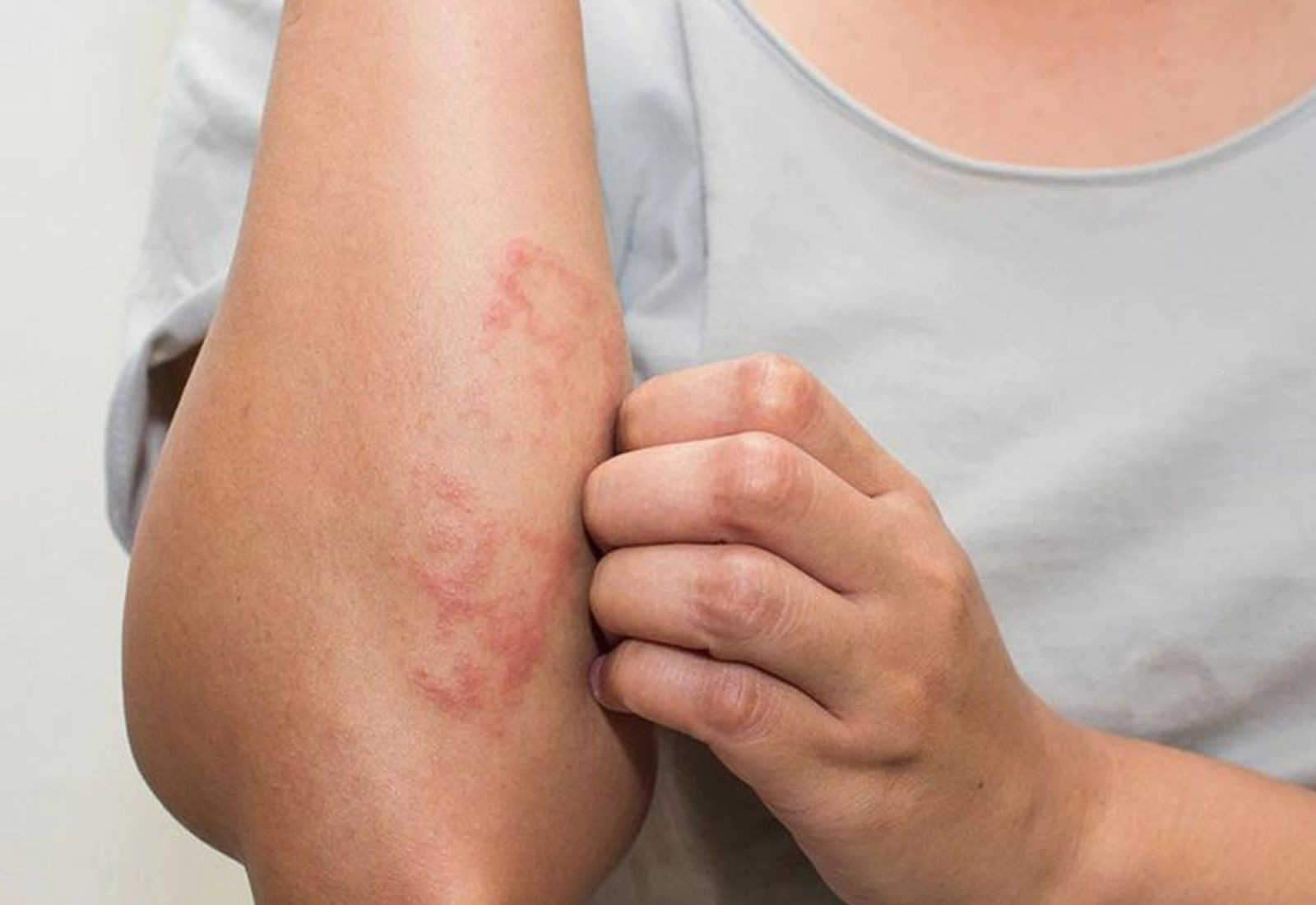
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) occurs when the body produces antibodies against its own components, called autoantibodies. In a patient’s body, these autoantibodies combine with antigens to form immune complexes. These complexes can deposit in the body and cause various dangerous symptoms for the patient. Without timely intervention, lupus can damage most organs in the body and can even be fatal.
However, diagnosing lupus can be challenging because the symptoms vary from case to case, change over time, and can easily be mistaken for other diseases. Therefore, to diagnose and monitor the treatment of lupus, patients may undergo the following lupus tests:
A complete blood count measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, as well as the hemoglobin level in red blood cells. This test helps doctors detect whether a patient has anemia or infection, both of which are common in lupus patients. Additionally, a low white blood cell or platelet count can also be a sign of lupus.
Measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a commonly used test in the clinical diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. This test determines how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube in one hour. A faster-than-normal sedimentation rate can indicate a systemic disease, such as lupus.

However, an elevated ESR is not specific to any particular disease. It can be elevated if you have lupus, an infection, or cancer.
A urinalysis can reveal elevated levels of protein or red blood cells in the urine, which may occur if lupus has affected the kidneys. Therefore, this test is considered useful in diagnosing lupus.
Evaluating liver and kidney function through blood tests can also aid in diagnosing lupus, as the disease can affect these organs.
The ANA test is one of the primary tests performed in diagnosing lupus. ANA are antibodies that bind to structures within the nucleus of cells, and they are not present in healthy individuals. ANA are found in patients with autoimmune diseases, including lupus. The purpose of the ANA test is to detect ANA in the blood of lupus patients, and about 95% of lupus patients test positive for these antibodies.
However, false positives can occur with this test. Therefore, the ANA test helps guide doctors in determining the cause of a patient’s symptoms.
A more specific test for lupus is the anti-DNA antibody test, which detects antibodies that directly target double-stranded DNA. Approximately 70-95% of lupus patients test positive for anti-DNA antibodies.
Among lupus diagnostic tests, anti-Ro (SSA) and anti-La (SSB) tests are highly specific as they target RNA. These two antibodies are also associated with neonatal lupus.
Pregnant women who test positive for anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies should be closely monitored by their doctor.
If a doctor suspects lupus is affecting the structure or function of the heart or lungs, certain imaging tests may be ordered, such as:
Lupus can damage the kidneys and also affect treatment methods. Therefore, in some cases, doctors may order a biopsy to determine the most effective treatment option. Occasionally, a skin biopsy is also performed to confirm how lupus is affecting the skin.
Patients suspected or confirmed to have lupus need to undergo lupus testing for several reasons, specifically:
The symptoms of lupus vary greatly from person to person and are easily mistaken for other diseases, making diagnosis challenging. No single test can definitively diagnose lupus. To diagnose it, doctors need to combine blood tests, urine tests, biopsies, and observe the patient’s clinical symptoms.
Sources:
https://mayoclinic.org
https://cdc.gov
https://hss.edu
24
Useful article?
Useful article?
24
Useful article?